ML for SWEs 67: No, there won't be a 3-day work week
CEOs predict AI will create a 3-day workweek
We’re only 5 paid subscribers away from bestseller status! The next 5 people can become a paid subscriber for only $10/yr forever. Thanks for all your support!
There’s a huge question mark right now about how work will be in the future. I find it especially interesting because there’s two parties discussing this topic that approach it from two different angles.
The first party is worried about an economy that leaves their skillset behind. This party worries about providing for their family. They worry about their ability to afford food and other basic necessities.
The second party discusses the positive impact of AI on the workforce. Multiple CEOs have predicted AI creating a 3-day workweek in the future giving everyone more time to do what they want while getting their work done in less. I can’t help but notice that this crowd always seems to be people who are well-off enough not to worry about what happens to them when their income dries up.
In reality, we don’t really know what the nature of work will be in the future. We can make predictions based on AI’s current impact on the workforce, but it’s hard to quantify the actual impact of AI versus the impact caused by the FUD/hype surrounding AI.
Here’s a quick low-down on what we don’t know, what we do know, and what we can most accurately predict about AI’s impact on the workforce:
What we don’t know:
How quickly advancements will happen and how soon after impact will follow. Even area experts find it difficult to predict how AI will have advanced in 6 months.
What that impact will be. If we can’t make the prediction mentioned above, how can we possibly accurately predict the impact on the workforce in the long-term?
Most predictions fall into this category. Good examples include: AI replacing software engineers 25 months ago (couldn’t find the link for this but its been all over X for a while) and 90% of code being written by AI by now.
What we do know:
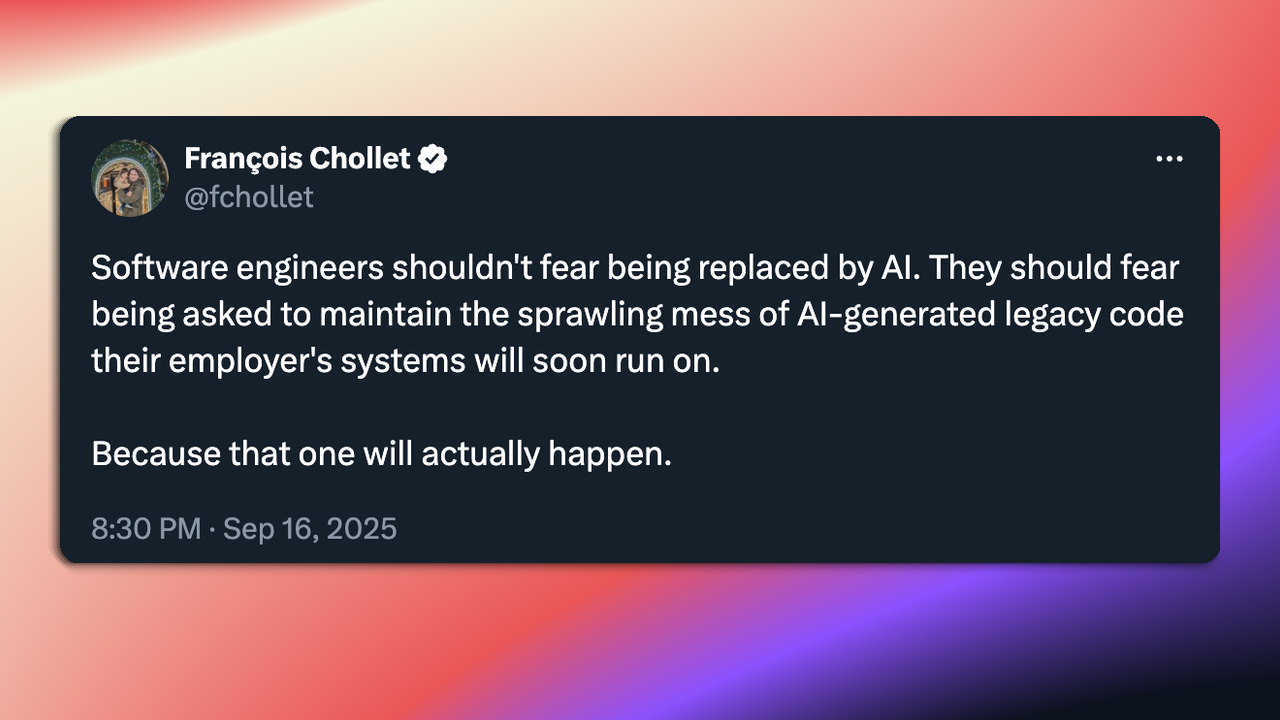
AI will transform the workforce. It absolutely can already replace certain jobs. Anyone who denies this is wrong. The best recent example of this is Nano Banana.
As AI is used, the importance of “why” something is being done and the higher-level thinking behind work becomes more important. The “what” and “how” are what we can most likely replace with AI.
What we can accurately predict:
AI will advance until it hits an absolute wall or society reaches post-scarcity. If you’re unfamiliar with the concept, follow that link to brush up on it. It’s what AI is aiming to achieve.
The current sentiment behind AI is to get more done faster. It is highly unlikely AI will create a society where humans do less work and much more likely to create a society where humans do more work in the same amount of time.
So what’s the takeaway from all of this?
As soon as you realize even the most seasoned AI veterans spend their time trying to understand how AI can be used and where AI will be more impactful, predictions about the future of AI become much more grounded in reality.
Usually, predictions are made to fit a narrative by people who are adjacent to the problem, but not directly involved in it. Those directly involved have their heads deep in the problem space trying to understand what’s going on instead of making up claims.
Practically speaking, you should know two things. First, no, we won’t have a 3-day workweek due to AI. For the second, I’ll leave you with this image below:
Sorry if the tone of this week’s ML for SWEs edition seems negative. I find myself frequently having to bring things back down to reality. AI is the world’s most important technology, but it can only live up to its potential if we approach is realistically!
Enjoy the rest of the resources! Last week, we discussed safety being a fundamental AI engineering requirement. If you missed it, you can catch that here:
ML for SWEs 66: Safety is a fundamental AI engineering requirement
Welcome to Machine Learning for Software Engineers. Each week, I share a lesson in AI from the past week, five must-read resources to help you become a better engineer, and other interesting developments. All content is geared towards software engineers and those that like to build things.
Must reads
Claude's new Code Interpreter: Claude's new Code Interpreter enables the creation and editing of files such as Excel spreadsheets, documents, and PDFs. The feature supports advanced data analysis and data science, including the generation of Python scripts and data visualizations. Claude executes custom Python and Node.js code within a server-side sandbox for data processing.
Defeating Nondeterminism in LLM Inference: Large language models struggle with reproducibility, often providing different results even when asked the same question. Even with temperature adjusted to 0 for greedy sampling, LLM APIs and OSS inference libraries do not produce deterministic outputs. One hypothesis attributes this nondeterminism to floating-point non-associativity on GPUs combined with concurrent execution.
The 5 AI-Related Jobs Every Software Engineer Should Know About: Five consolidated AI-related roles are AI Research Scientist, Research Engineer, Machine Learning Engineer, Software Engineer, AI, and AI Engineer. AI research scientists conduct original research to advance AI capabilities, focusing on novel AI capabilities through experimentation and a research workflow. A PhD or sometimes an MS in a related field and deep research experience in a relevant AI field are qualifications for an AI Research Scientist.
How AI is helping 38 million farmers with advance weather predictions: The University of Chicago employs NeuralGCM, a Google Research model, for predicting India's monsoon season. NeuralGCM combines traditional physics-based modeling with machine learning. 38 million farmers in India received AI-powered forecasts regarding the monsoon season's start.
Fully autonomous robots are much closer than you think – Sergey Levine: Sergey Levine is one of the world’s top robotics researchers and a co-founder of Physical Intelligence. He believes fully autonomous robots are much closer than commonly perceived. Levine indicates the field is on the cusp of a "self-improvement flyw."
Other interesting things this week
AI Developments
Listen to a discussion on how AI can power scientific breakthroughs.: Logan Kilpatrick hosts the Google AI: Release Notes podcast. Pushmeet Kohli leads Google DeepMind’s science and strategic initiatives team. A team's problem-solving framework produced AlphaFold and AlphaEvolve; AI co-scientist is a new tool intended to enable breakthroughs.
Social media promised connection, but it has delivered exhaustion: Social media feeds display repetitive stock portraits, generic promises, and recycled video clips across platforms. Algorithmic prioritization sidelines genuine human content, leading engineered content and AI-generated material to receive more interactions. The focus of these feeds has shifted from people to consumers and content consumption.
On China's open source AI trajectory: China is maneuvering to double down on its open AI ecosystem. Chinese AI models including Qwen, Kimi, Z.ai, and DeepSeek demonstrated dominance in open models during the summer. Prior to the DeepSeek moment, AI was likely a fringe issue for the PRC Government.
The latest AI news we announced in August: Google made many AI advancements in August. AI Mode in Search expanded to more countries, and Deep Think became available in the Gemini app. New Pixel hardware with advanced AI features was released, and AI learning tools became free for college students.
Product Launches
Introducing upgrades to Codex: OpenAI has updated Codex to make it faster and more reliable in all its formats (web, IDE, CLI). They’ve also released GPT-5-Codex, a GPT-5 model optimized to be an independent coding agent.
How AI made Meet’s language translation possible: Google Meet now features real-time language translation, built collaboratively by Google Meet, DeepMind, and Research teams leveraging AI. This Speech Translation feature converts spoken language in near real-time, available in Italian, Portuguese, German, and French.
Claude now has access to a server-side container environment: Claude can create and edit Excel spreadsheets, documents, PowerPoint slide decks, and PDFs directly in Claude.ai and the desktop app. File creation is available as a preview for Max, Team, and Enterprise plan users, with Pro users gaining access in the coming weeks. Claude creates actual files from instructions, processing uploaded data, researching information, or building from scratch.
Tools and Resources
The latest Google AI literacy resources all in one place: Google is building AI literacy programs and resources for parents, educators, and students, accessible in a new AI Literacy hub. A new podcast, "Raising kids in the age of AI," created with aiEDU, will release episodes beginning September 25. A new video series demonstrates using Google's AI features, including Guided Learning, for homework assistance and custom study guides.
How to Build Agentic AI 2 (with frameworks) [Agents]: Devansh wrote the material, published on September 12, 2025. A previously published guide for Agentic AI construction is being reshared. The "Chocolate Milk Cult" community reaches over one million members each month.
Toddlerbot: Open-Source Humanoid Robot: ToddlerBot is a low-cost, open-source humanoid robot platform. It is designed for scalable policy learning and research in robotics and AI.
DOOMscrolling: The Game: A web browser game inspired by Doom was developed, playable solely through scrolling. An initial attempt to create the game using LLMs failed nine months prior, with GPT-4 misinterpreting scrolling direction for background movement. A functional prototype was later created in two hours with GPT-5, following a broad design description that compared it to an upside-down Galaga.
AI Roundup 135: Feature parity: ChatGPT gained the ability to use MCP clients, and Claude received access to a code sandbox with file reading and creation. Both features carry warnings about prompt injections, data destruction risks, and malicious connectors.
Research and Analysis
How People Use ChatGPT [pdf]: An excellent overview of how people are actually using ChatGPT and similar LLM tools and apps.
How to Analyze and Optimize Your LLMs in 3 Steps: A three-step process exists for analyzing and optimizing Large Language Models (LLMs) after production deployments. This process involves analyzing LLM outputs, iteratively improving areas with the most value to effort, and evaluating and iterating. Step 1, analyzing LLM outputs, can utilize manual inspection, grouping queries by taxonomy, or an LLM as a judge on a golden dataset.
How to Train Graph Neural Nets 95.5x Faster[Breakdowns] by
: Changing data representations enhances AI system performance, a principle behind techniques like Feature Engineering, Prompting, and Context Engineering. These methods alter how a model perceives input to achieve superior responses. Prompting guides Large Language Model generations in the semantic space.- : Algorithm analysis involves determining an algorithm's correctness, its cost, and whether a better alternative exists. An algorithm taking 3N steps is considered equivalent to one taking N steps. Alice devised a solution to a public challenge by checking every possible start and end day, summing duel results for each period.
Why accessibility might be AI’s biggest breakthrough: The UK's Department for Business and Trade conducted a Microsoft 365 Copilot trial between October 2024 and March 2025. Neurodiverse employees reported statistically higher satisfaction and were more likely to recommend the tool than other participants. The study also noted benefits for users with hearing disabilities and suggests AI tools may address workplace accessibility gaps.
Claude’s memory architecture is the opposite of ChatGPT’s: Claude's memory system starts each conversation with a blank slate and activates only when explicitly invoked. It recalls information by referring to raw conversation history, without using AI-generated summaries or compressed profiles. When memory invocation occurs, Claude deploys retrieval tools to search past chats in real-time.
Infrastructure and Engineering
How DoorDash uses AI Models to Understand Restaurant Menus: DoorDash uses large language models (LLMs) to automate the process of turning restaurant menu photos into structured data. This automation addresses the challenge of keeping menus updated, which is costly and slow when done manually at scale. The project's technical goal is accurate transcription of menu photos into structured menu data with low latency and cost for production at scale.
Accelerate Protein Structure Inference Over 100x with NVIDIA RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell Server Edition: Since AlphaFold2's release, AI inference for determining protein structures has skyrocketed. CPU-bound multiple sequence alignment generation and inefficient GPU inference remained rate-limiting steps despite these advancements. New accelerations developed by NVIDIA Digital Biology Research labs enable faster protein structure inference using OpenFold at no accuracy cost compared to AlphaFold2, utilizing the NVIDIA RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell Server Edition GPU.
Security and Governance
9 Best Practices for API Security ⚔️: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) sends data in plaintext without encryption. This allows information on a public network to be easily accessed or changed.
Anthropic Might Legally Owe Me Thousands of Dollars by
: Anthropic reached a $1.5 billion copyright settlement, covering approximately 500,000 books. This settlement allocated $3,000 per work to book authors whose works were allegedly pirated to train Anthropic's AI systems. The company reportedly downloaded these books without permission from "shadow libraries" such as LibGen and PiLiMi.Modeling Attacks on AI-Powered Apps with the AI Kill Chain Framework: AI-powered applications introduce new attack surfaces not fully captured by traditional security models. The NVIDIA AI Kill Chain consists of five stages—recon, poison, hijack, persist, and impact—and focuses on attacks against AI systems.
Career and Industry
A joint statement from OpenAI and Microsoft: On September 11, 2025, OpenAI and Microsoft signed a non-binding memorandum of understanding for the next phase of their partnership. The companies are actively working to finalize contractual terms in a definitive agreement. Their joint focus remains on delivering AI tools for everyone, grounded in a shared commitment to safety.
Thinking Machines becomes OpenAI’s first services partner in APAC: Thinking Machines Data Science is joining forces with OpenAI as its first official Services Partner in the Asia Pacific region. This collaboration helps businesses in APAC turn artificial intelligence into measurable results. The partnership offers executive training on ChatGPT Enterprise, support for building custom AI applications, and guidance on embedding AI into operations.
Zoom CEO predicts AI will lead to a three-day workweek: Zoom CEO Eric Yuan predicts that AI automation will lead to a three-day workweek, fundamentally altering the nature of human jobs and freeing up people to focus on more creative and strategic endeavors.
OpenAI Grove: OpenAI announces a program that allows individuals building with AI to work closely with AI researchers. It focuses on creating a talent-dense network and providing resources for participants.
If you found this helpful, consider supporting ML for SWEs by becoming a paid subscriber. You'll get even more resources and interesting articles plus in-depth analysis.
Always be (machine) learning,
Logan